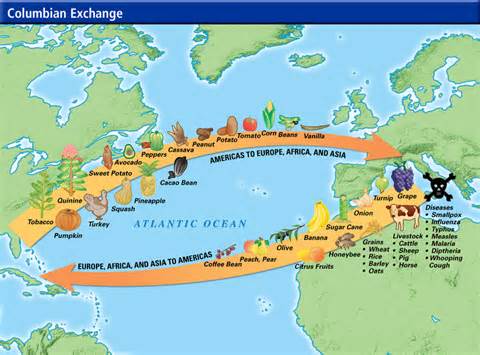
The Taíno impact in the Columbian exchange was linguistically, biological, and cultural. Linguistically, words used in today’s everyday language come from the Taíno culture such as barbeque, cannibal, hurricane, savanna, and cacique. In other parts of the world, including present day Puerto Rico, the Taíno language is far more extensive with names of plants, tress, fruits, fish, animals, birds, objects, and instruments.
Cultural influences include the spreading of cassava to other regions such as sub-Saharan Africa, India and Southeast Asia. In addition, maize is a common good in Spain, central Europe, and the Mediterranean Basin. Other foods include the sweet potato, bean, squash, peanut, guava, mamey, and pineapple. Goods that were part of the Columbian exchange consist of rubber, tobacco, rubber-ball games, canoes, and the hammock.
As a result of the Spanish conquest over the West Indie islands, the exchange impacted biological assimilation as well. Here, Taíno women were married off to Spanish men and freed African slaves. The result of this is a mixed race that, today, claims partial Taíno decent.
(Bauer, Lugo, & Robinson, 2014; Rouse, 1992)